Low ice, low snow, both poles
http://nsidc.org/arcticseaicenews/
http://nsidc.org/arcticseaicenews/files/1999/06/Figure-3-350×270.png
Daily Arctic sea ice extents for May 2016 tracked two to four weeks ahead of levels seen in 2012, which had the lowest September extent in the satellite record. Current sea ice extent numbers are tentative due to the preliminary nature of the DMSP F-18 satellite data, but are supported by other data sources. An unusually early retreat of sea ice in the Beaufort Sea and pulses of warm air entering the Arctic from eastern Siberia and northernmost Europe are in part driving below-average ice conditions. Snow cover in the Northern Hemisphere was the lowest in fifty years for April and the fourth lowest for May. Antarctic sea ice extent grew slowly during the austral autumn and was below average for most of May.
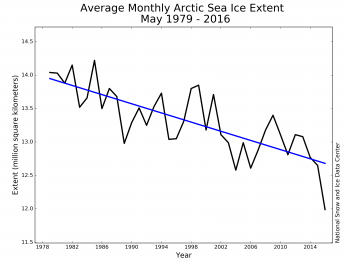
May 2016 set a new record low for the month for the period of satellite observations, at 12.0 million square kilometers (4.63 million square miles), following on previous record lows this year in January, February, and April. May’s average ice extent is 580,000 square kilometers (224,000 square miles) below the previous record low for the month set in 2004, and 1.39 million square kilometers (537,000 square miles) below the 1981 to 2010 long-term average.
During the month, daily sea ice extents tracked about 600,000 square kilometers (232,000 square miles) below any previous year in the 38-year satellite record. Daily extents in May were also two to four weeks ahead of levels seen in 2012, which had the lowest September extent in the satellite record. The monthly average extent for May 2016 is more than one million square kilometers (386,000 square miles) below that observed in May 2012.