Hidden World of Bacteria and Fungi Discovered on Leonardo da Vinci’s Drawings
By By Rafi Letzter | Live Science Staff WriterNovember 20, 2020 | Leonardo da Vinci is famous for his elaborate, nuanced artworks and advanced technological ideas. But new research has revealed another level of complexity to his drawings: a hidden world of tiny life-forms on his artwork.
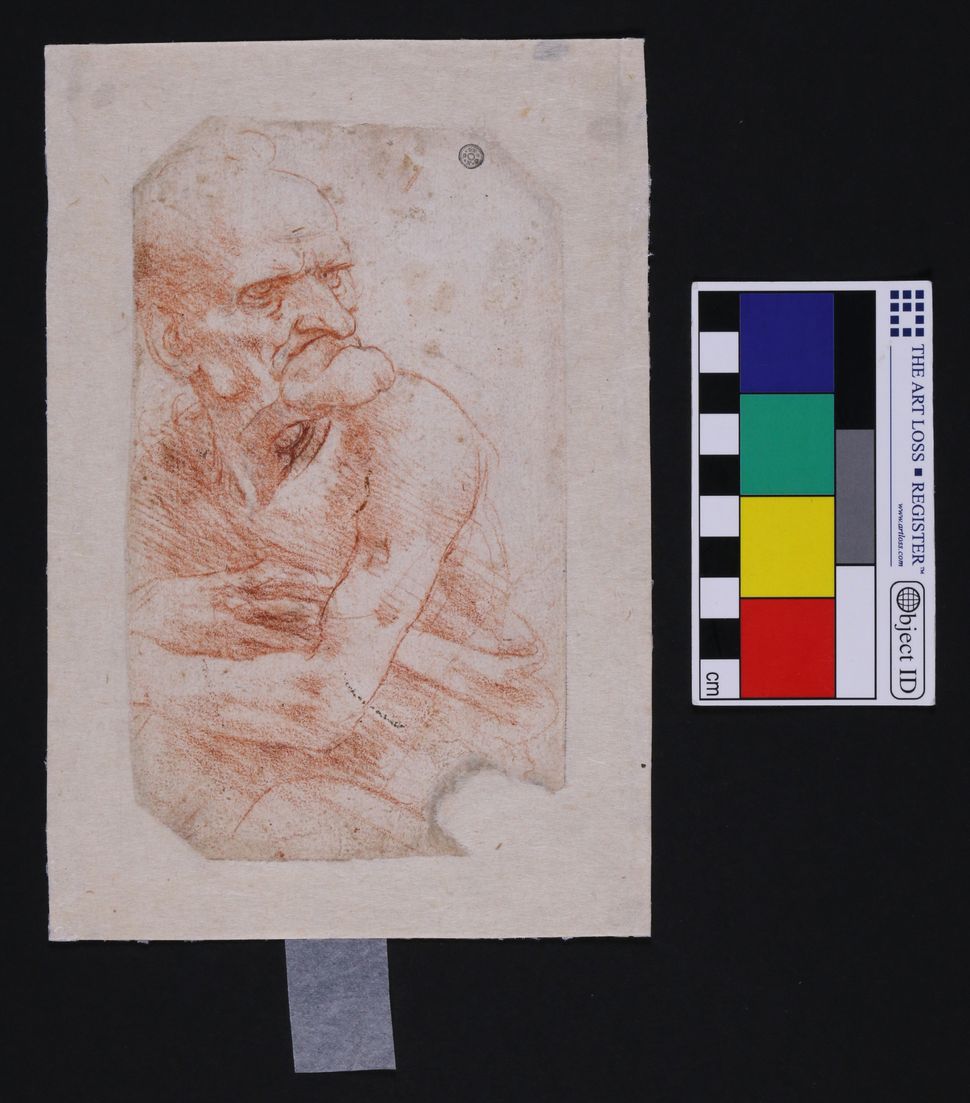
This is Leonardo Da Vinci’s “Uomo della Bitta,” one of six drawings by the master recently revealed to host complex microbiomes.
(Image: © Pinar et al.)The findings, the researchers said, could help build a microbiome “catalogue” for artwork. Each of the pieces had a unique enough collection of microbes that researchers could have identified it again later purely from a study of its microscopic biology. And the drawings’ microbiomes had enough key elements in common to help researchers spot counterfeits based on differences in their microbiomes, or even authentic drawings that had been stored in different conditions over the centuries. The researchers also showed that da Vinci’s drawings had a significantly different microbiome than expected, with lots of bacteria and human DNA — likely a consequence of centuries of handling by art restorers and other people. Microbes known to make paper degrade over time were also present, showing why those restorers’ efforts had been necessary The study amounts to a proof-of-concept exercise, showing how microbiomes might, in the future, reveal unexpected histories of certain artworks or help detect forgeries.
Researchers examined the microscopic biological material, living and dead, in seven of the master’s “emblematic” drawings, and found an unexpected diversity of bacteria, fungi and human DNA. Most of that material probably landed on the sketches well after da Vinci’s death 501 years ago, so the DNA (or the bulk of it at least) likely comes from other people who have handled the drawings over the centuries and not the polymath himself. But the newfound biological materials do have a story to tell.