https://nsidc.org/arcticseaicenews/
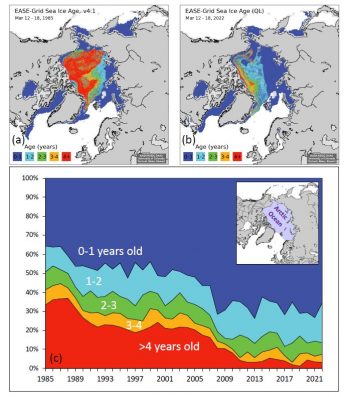
With the onset of spring, it is time again for a check-in on sea ice age—the number of years that a parcel of ice has survived summer melt. As noted in previous posts, ice age provides a qualitative assessment of thickness, as older ice has more chances to thicken through ridging, rafting, and bottom ice growth (accretion) during winter. The coverage of the old, thick ice has a significant control on how much total ice survives the summer melt season—the first-year ice that grows thermodynamically over winter is more easily melted away during summer. That which survives through the summer melt season grows in age by one year. The extent of old ice declines through the winter when it drifts out of the Arctic through the Fram or Nares Strait. At the end of last summer, the extent of the oldest ice (greater than 4 years old) tied with 2012 for the lowest in the satellite record. This spring, we continue to see a dominance of first-year ice (Figure 4). The percentage of the greater than 4-year-old ice, which once comprised over 30 percent of the Arctic Ocean, now makes up only 3.1 percent of the ice cover.
If you have trouble reading the graphic, go to the link above and click on “high-res image”.