There are Two Kinds of Sunspots on the Sun Right Now Amid Solar Cycle Change
The sun can’t make up its mind.
By Meghan Bartels | Senior WriterSPACE.COM – May 4, 2020 | The sun offers plenty of brainteasers: Right now, for instance, it’s sporting magnetic knots formed by two different cycles — simultaneously.
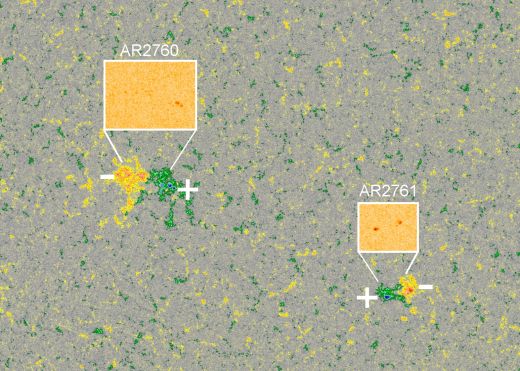
Two active regions on the sun with opposite magnetic fields: 2760 matches solar cycle 24 while 2761 matches solar cycle 25. (Image credit: Tony Phillips/spaceweather.com)This ambiguity is a common characteristic of the period called the solar minimum, when the sun is least active. The solar minimum falls at the dip between two solar maximums, with a full minimum-to-maximum-to-minimum cycle lasting about 11 years. As the solar activity cycle rolls, magnetic activity on the sun first rises, then falls, and each cycle has an opposite magnetic flavor to the last.
Solar activity is characterized by the sun’s surface being pockmarked by cooler, dark regions called sunspots, some of which release massive bursts of light or charged particles. In between maximum periods, like now, the sun is mostly quiet, but what activity there is can resemble that of either the previous or the upcoming solar cycle.
“During the time that the one cycle fades and the other cycle begins, you kind of see an overlap,” W. Dean Pesnell, project scientist of the Solar Dynamics Observatory, told Space.com. “At the current time, we are seeing that with two active regions.”