Effect Predicted by Albert Einstein Spotted in a Double-Star System
This effect, known as gravitational red-shift, is critical for maintaining GPS on Earth.
By Chelsea Gohd | SPACE.com Staff WriterOCTOBER 27, 2020 | Gravitational redshift, an effect predicted by Albert Einstein that is crucial for maintaining the Global Positioning System (GPS) on Earth, has been observed in a star system in our galaxy.
Within Einstein’s general theory of relativity there is an effect known as “gravitational redshift,” in which light becomes redder because of the influence of gravity; the wavelength of a photon, or light particle, gets longer and appears redder as the wavelength climbs farther away from a gravitational well.
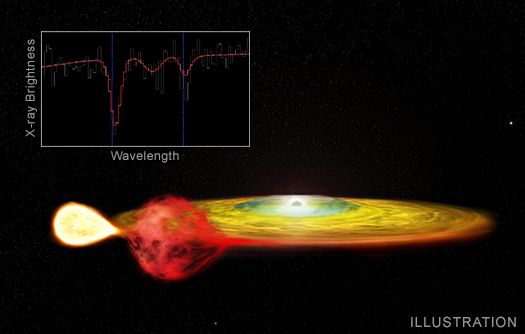
Scientists have observed gravitational redshift, an effect predicted by Albert Einstein in the double star system 4U 1916-053. (Image credit: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss)A gravitational well is the pull of gravity exerted by large bodies in space, like Earth. Under this effect, clocks on Earth’s surface actually run slower than clocks far away and experiencing less gravity, so clocks on orbiting satellites run slower. Because of this, redshift has to be factored into calculating positions on Earth with GPS.
Now, while scientists have found absolute evidence of this effect in our solar system, they have found less evidence farther away because the observations are more difficult to make. But now, in a new study, researchers have spotted gravitational redshift in a two-star system a whopping 29,000 light-years (200,000 trillion miles or 321868800000000 kilometers) away called 4U 1916-053.