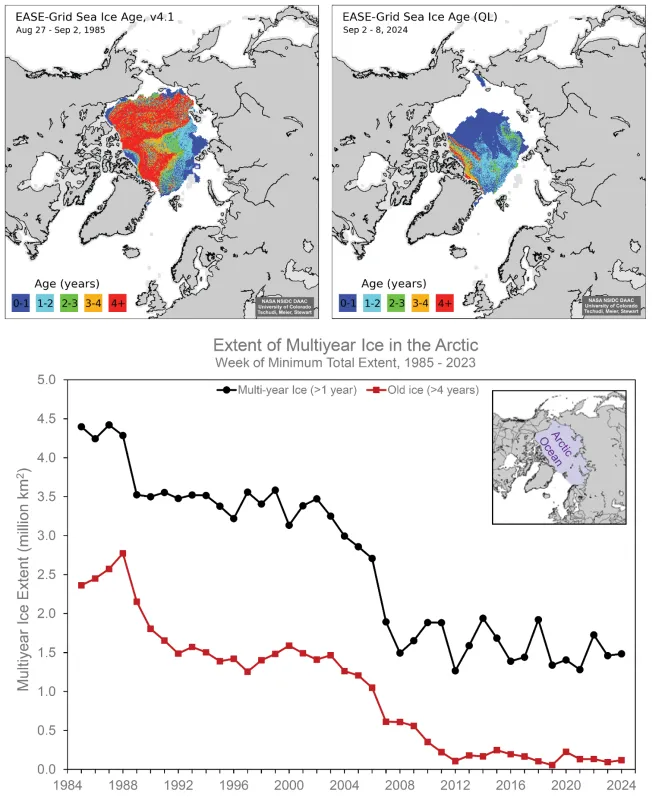
Its the upper graphic, the map comparison, that tells the story here. “Old” sea ice refers to ice that has survived more than one season, that is, it has managed to persist as sea ice through the summer melt. Old ice serves as a means of keeping the Arctic ocean waters cool and by reflecting solar radiation back into space, and to serve as a nucleus around which new ice may form as fall and winter arrive. It is also thicker, as a rule, than young ice more recently formed. It gives a measure of the volume of ice floating on the sea. In satellite imagery, it is impossible to distinguish between old and young ice, but new satellite radiometer sensors can.
In these images, the color coding indicates the age of the ice. The older ice is generally thicker, and gives a more realistic picture of the amount of ice covering the polar sea. The bottom graph tells us the old sea ice coverage has pretty much bottomed out, starting around 2008. The ice we see at the north pole now is mostly young ice, thin and low volume. Multi-year ice has pretty much leveled off at about 1.5 million km^2, while old (>4 year)sea ice coverage is now negligible.
Data from nsidc.com